Rebates at Lowest Level Ever
The lowest number of monthly rebates since its inception has been awarded by CHEAPR in April 2020, a not so grand total of 13, down from 90 in March.
There is almost no public reporting anymore of monthly new vehicle sales, but we know the automotive sector rapidly plunged in the latter half of March, which was felt over the duration of April. There have been some reports of a modest uptick in May.
Following the counter-intuitive increase in rebates in March (relative to Jan. and Feb.), when the rest of the world was collapsing, this is probably more in line with what will be the new normal for the time being. 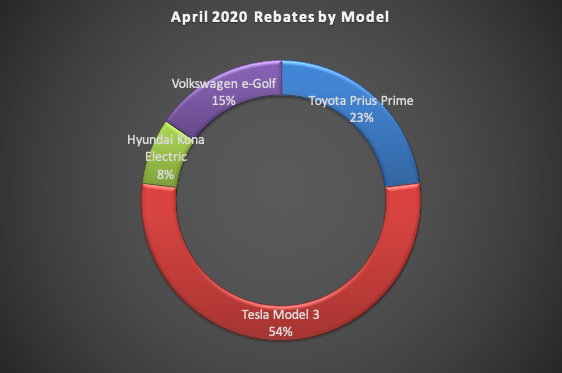 Tesla so dominates the EV market, as well as being the only manufacturer to post a sizable YOY sales increase in Q1, that how many Model 3s are rebate eligible is mostly what determines where the trend goes. It is also possible that some Model 3 supply disruption due to the temporary closure of the Fremont plant is part of the reason, as well. The Model 3 accounted for 54% of April rebates, which translates to all of 7. General Motors has been heavily discounting the Chevy Bolt, but there were no Bolt rebates in April.
Tesla so dominates the EV market, as well as being the only manufacturer to post a sizable YOY sales increase in Q1, that how many Model 3s are rebate eligible is mostly what determines where the trend goes. It is also possible that some Model 3 supply disruption due to the temporary closure of the Fremont plant is part of the reason, as well. The Model 3 accounted for 54% of April rebates, which translates to all of 7. General Motors has been heavily discounting the Chevy Bolt, but there were no Bolt rebates in April.
CHEAPR Way Under Budget
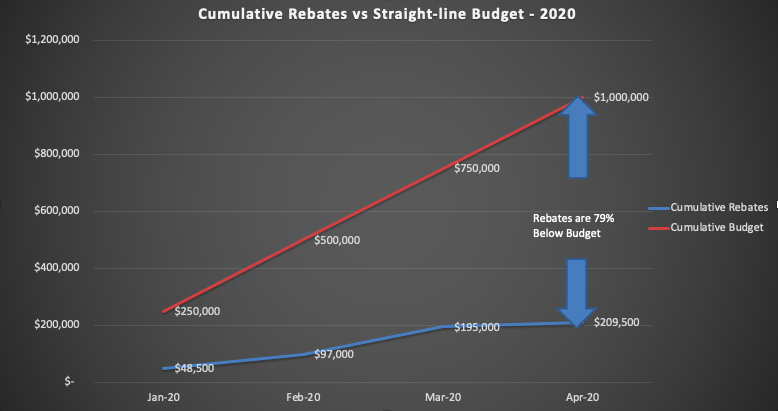
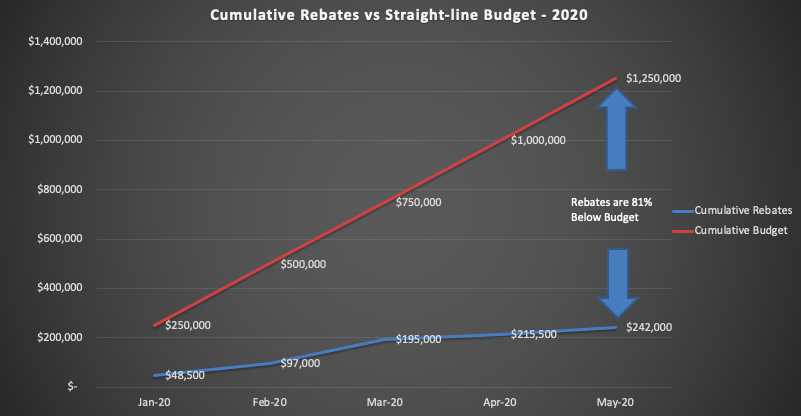
This blog has been critical of the drastic restrictions imposed on rebate parameters in October 2019. DEEP told us at the Tesla Leasing Event in February that they were concerned that funds would run dry. That was a 3-month problem (Oct – Dec. 2019) until the new funding started, but the new CHEAPR board has yet to course-correct, despite pacing hugely under budget.
The CHEAPR budget is $3 million annually and there are no rules about how it is supposed to pace. There are good reasons for carefully managing the budget. Temporary funding disruptions are, well, disruptive. However, if we look at the budget on a straight-line cumulative basis and compare it to the dollar amount issued for rebates, by that definition it is pacing 79% below budget.
There is also the consideration of a forthcoming rebate for used EVs. To this point, there has been no announcement, and we are doubtful there will be one anytime soon because the Roadmap recommends that an outside contractor be engaged to design and implement it, meaning this presumably hasn’t happened yet. We also expect that an incentive for a used EV will be lower than for a new vehicle, and will include an income cap, as well as a lower MSRP cap. We don’t see this as a budget-buster.
EV Roadmap and CHEAPR
The subject of purchase incentives is accorded 15 pages in the EV Roadmap and it traces the origins and thinking about the program. It is still true today, as it was in 2015 when CHEAPR was begun, that while battery prices are on a downward trajectory, EVs have not yet reached cost-parity with ICE vehicles. Cited in the Roadmap is a stat from the Multi-State ZEV Action Plan that there was an average purchase price difference of greater than $10,000 between comparable EV and ICE vehicles in 2016. While EVs cost less to run and maintain, this headline price difference is a real barrier.
I have to say that it was a surprise to learn from the Roadmap that until 2020, CHEAPR was a pilot. For 5 years. Well, okay. With the legislation that was passed last year, it is now reconstituted with an independent board that remains situated in DEEP for administrative purposes.
Something that has changed is that two manufacturers, Tesla and General Motors, have exceeded the unit sales threshold for the federal EV tax credit and have passed beyond the phase-out period. There is no federal incentive for vehicles from these two manufacturers. The Roadmap cites projections from EVAdoption that indicate the next automaker to cross the sales threshold will be Nissan in the latter half of 2021. (This projection predates the COVID-19 crisis.) Attempts in Congress to modify the program and raise the threshold have not met with success. In this context, CHEAPR assumes a larger role.
Value of Purchase Incentives
The EV Club of CT is a supporter of CHEAPR and available data indicate that incentives matter. CHEAPR has handed out 5,984 rebates through April 30, 2020. Given that there were 11,677 EVs registered in the state as of Jan 1, 2020, the program looks to have played a meaningful role. Survey-research of rebate recipients reports that over 80% of respondents cite the incentive as being either extremely or very important to their decision to acquire an EV.
The Roadmap cites experiences of similar programs in other states. One of them is Georgia, which has been cited previously in this blog, as a dramatic example of a “light switch test.” When Georgia lawmakers rescinded a generous tax credit of $5,000 and added an annual EV fee, sales fell off a cliff. This is a graphical representation of what happened that was published on page 89 of the Roadmap. 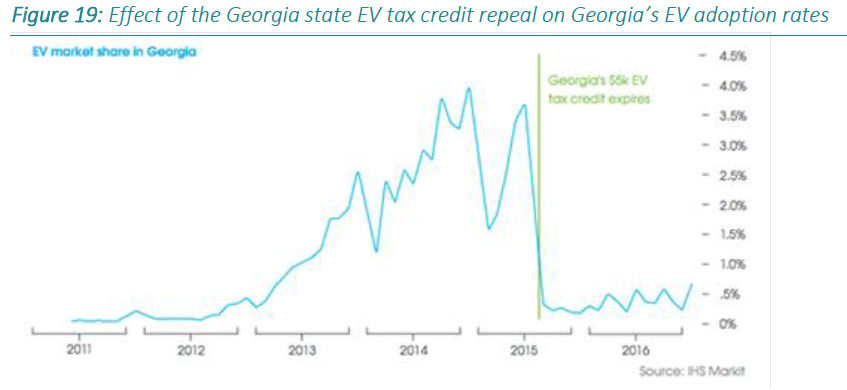
Rebate Parameters
There are several variables that go into how much of a rebate if any, a given EV purchaser qualifies for, which we are calling rebate parameters (and which DEEP refers to as “bins).
- Available funding
- Rebate size and tiers
- MSRP cap
- Future consideration of a rebate for used EVs, along with a likely income cap.
- One rebate lifetime per licensed driver
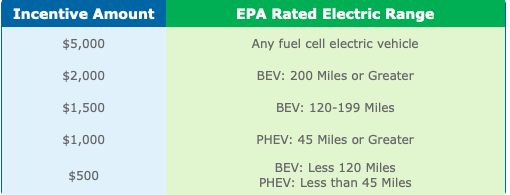
Rebates are offered for battery electric vehicles (BEV), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV), and Fuel-Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEV). Rebate parameters have changed several times since the program began. The size of the rebate was originally pegged to the size of the battery pack but was modified in 2017 to be based on EPA-rated electric range. Battery pack size is not directly indicative of the range, so this approach makes sense. Also, over time, there are changes in technology (substantially longer ranges) and other aspects of the environment that gradually, but consistently, evolve.
The MSRP cap initially was $60,000. It was changed to $50,000 in October of 2018 and then to $42,000 where it currently stands. Rebate tiers are currently $5000 for any FCEV, $1500 for a BEV with a range of at least 200 miles, $500 for a BEV with a range of fewer than 200 miles, and $500 for any PHEV.
The number of rebates awarded has declined significantly since the October change and it is obviously because the lower level now excludes almost all trim levels of the Model 3. This blog has discussed this previously on April 2nd and in earlier posts.
We also noted that the lowering of the MSRP caused a shift in the mix of rebates toward PHEVs, which we discussed here. (April is the low-volume exception.) But you wouldn’t know this from the Roadmap, which on page 83, contains this exhibit of rebates by fuel-type.
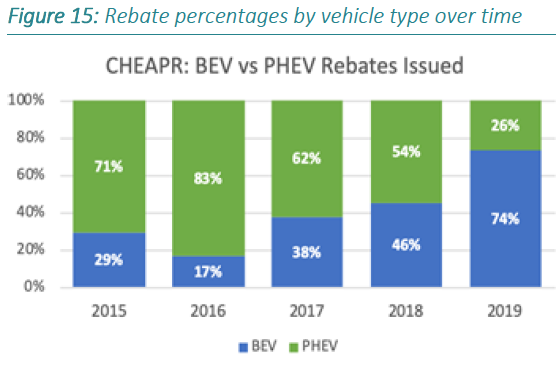
The footnote indicates that the rebate data had been updated through July 26, 2019, in other words, before the changes were made. It seems clear that lowering the MSRP cap was counter-productive, both from the perspective of consumers being able to use the rebate along with making the funds less efficient in terms of zero-emission miles subsidized. The market in general is trending toward BEVs which may eventually change things. But we strongly feel that the MSRP should be raised to at least $50,000 (same as MA) or higher (NJ is $55,000 and NY is $60,000). The rebate levels could be left in place while the run-rate is evaluated with the higher MSRP, whatever modeling has been done for used EVs, and projections for when this depressed market normalizes. We are not aware of the law allowing unused funds from one year to be carried forward.
Dealer Incentive
A headline that appeared over a NY Times story in 2015 read, “A Car Dealers Won’t Sell: It’s Electric.” The unwillingness of many dealers to sell EVs has been a persistent bottleneck. So the idea that DEEP included in the original CHEAPR formulation a $300 incentive that would go to the dealership for each EV sold seemed a worthwhile experiment. It may sound slightly farcical to pay a business that is in the business of selling cars to sell cars, but if that is what it takes to seed change, so be it.
The incentive was subsequently lowered from $300 to $150. In the Roadmap, DEEP openly questions whether it is worth it and whether the funds would be better allocated to consumers to stretch what is a modest budget when compared to incentives in other states. (For example, the New Jersey per capita funding is 50% higher.) DEEP also found that the majority of the incentives were kept by the dealership, i.e. not given to the salespeople, which was kind of the basic idea.
This was underscored by two EV Shopper Studies done by the Sierra Club in 2016 and 2019. In the latter study, it was found that 74% of dealers did not have a single EV on the lot. The study did not report out CT separately (only CA had sufficient sample size for that) but in the 2019 study, there were no local dealers among those visited in the research that scored the highest rating. Our EV Club does know of some dealerships that do a good job with EVs and we appreciate them. We just wish they were the norm and not the exception.
VW Works Around Its Dealers in Germany
The most interesting recent development is from VW in Germany. They have announced that VW corporate will take responsibility for selling EVs and the dealers will only act as agents. Dealers will arrange test drives and deliver the car, but will not otherwise be part of the sales process. They will receive a fee for each vehicle they deliver and they will not have to buy the car. This last part is particularly interesting because it eliminates the risk of having to carry the cost of financing the vehicle if it is a slow-seller. It is the closest one can come to direct sales while still maintaining the franchise sales model and implicitly acknowledges its limitations. Here is a more detailed description published in ChargedEVs.
Dealer Recognition Program
Instead of the dealership financial incentive, we endorse DEEP’s proposal to work with the CT Auto Retailers Association (CARA) and create a dealer recognition program. If this is promoted to the consumer, it could serve to avoid some of the negative feedback loop that currently exists. We encourage that care is taken in giving this award so it isn’t vaporware. EV Club of CT works with the Sierra Club to conduct its EV Shopper Studies and our feedback to them will be to separately track visits to dealerships that are recognized in this way to see if their actions match the certification.
Fuel-Cell Electric Vehicle Incentive
CHEAPR has included FCEVs in its incentive plan from the beginning when incentives were set at $3,000. In July of 2016, the FCEV incentive was raised to $5,000. And when the MSRP cap was lowered to $42,000 for EVs, it was raised to $60,000 for FCEVs (they’re more expensive).
There have been exactly zero of these incentives awarded and there is a total of 3 FCEVs registered in the state. There is only 1 public hydrogen refueling station in CT.
FCEVs were dropped from the federal tax credit in 2017.
The rationale in the Roadmap is to support all promising new technologies and DEEP recommends continuing these levels for FCEVs for the duration of the current funding, which is through 2025. Their goals are modest: 591 FCEVs in the fleet and 6 or 7 refueling stations in the state by 2025. Keep in mind that a hydrogen refueling infrastructure has to be built from scratch. The other rationale that we have heard is that FCEVs have a longer range (and a short refueling time if you can find a place to fill up). The range part of that used to be the case, but now the longer-range BEVs have a similar range as FCEVs and higher mpg-e. Certainly, the differential in incentive can no longer be justified by range alone.
This blog is not against FCEVs, which are zero-emission vehicles. We do feel that DEEP/CHEAPR over-emphasizes them and, at times, uses them to represent CHEAPR in an intellectually dishonest way. At the Tesla Leasing Event in February, the DEEP spokesperson said that the CHEAPR program offers rebates of up to $5,000. It may be a convenient headline, but it is only true in the narrowest technical sense. For all practical purposes, the max rebate is currently $1500. And almost no Tesla qualifies for even that.
This is a link to the Roadmap. DEEP recommendations for CHEAPR are on page 92. We won’t repeat them here.
As we have made clear, these are our priorities:
- Raise the MSRP cap.
- Move quickly to implement an incentive for used EVs.
- Raise rebate levels, funds permitting.
- Eliminate the dealer incentive and re-purpose those funds for consumers.
- Develop guidelines for a dealer recognition program, which hopefully includes some input from consumers.
- Publish rebate data at the dealership level as they do in New York. Arguably, that alone is a dealer recognition program.
- Make e-bikes eligible for incentives under CHEAPR.
And, finally, one area where we are in agreement with the Roadmap, is to look to the future and the potential for leveraging incentives by partnering with utilities, as part of TCI, and with the manufacturers.
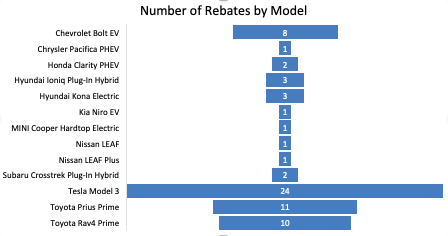
 Tesla so dominates the EV market, as well as being the only manufacturer to post a sizable YOY sales increase in Q1, that how many Model 3s are rebate eligible is mostly what determines where the trend goes. It is also possible that some Model 3 supply disruption due to the temporary closure of the Fremont plant is part of the reason, as well. The Model 3 accounted for 54% of April rebates, which translates to all of 7. General Motors has been heavily discounting the Chevy Bolt, but there were no Bolt rebates in April.
Tesla so dominates the EV market, as well as being the only manufacturer to post a sizable YOY sales increase in Q1, that how many Model 3s are rebate eligible is mostly what determines where the trend goes. It is also possible that some Model 3 supply disruption due to the temporary closure of the Fremont plant is part of the reason, as well. The Model 3 accounted for 54% of April rebates, which translates to all of 7. General Motors has been heavily discounting the Chevy Bolt, but there were no Bolt rebates in April.